What does bioavailability mean?
Bioavailability means how well can your body absorb specific ingredients and can use it for where it is needed.
Why does bioavailability matter in supplements?
With supplements, bioavailability is an important indicator of quality. This has everything to do with the fact that you take most supplements orally. It then undergoes all kinds of steps in the digestive process. The digestive process starts in your mouth, then goes to the stomach and continues to the intestines. In the stomach, stomach acids and digestive enzymes will act on the supplement and later the intestines add more digestive enzymes. It is important that a supplement can withstand these processes, otherwise you will no longer benefit from it and it would be a waste of money.
Many factors influence the bioavailability of supplements. The checklist below will help you make the right choice!
Want to make it easy on yourself? At LiveHelfi we have already done this check for you and therefore you will only find the highest bioavailable supplements in our webshop.
Which vitamin forms absorb best?
With vitamins, it is important to choose the right form. You can distinguish between the active form and precursors. The active form is the form that actually performs the function; precursors have to be converted by the body into the active form. Let’s have a look at the different forms of certain vitamins.
Vitamin A
Available as retinol (inactive vitamin) and beta-carotene (provitamin; precursor retinol) from plants.
Retinol is closer to the active form of vitamin A (active faster) and absorption is better than beta-carotene.
Vitamins B1 and B5
For vitamins B1 (thiamine) and B5 (pantothenic acid), absorption is already very good, and the form makes little difference.
Vitamin B2
There are three different forms of vitamin B2: riboflavin, riboflavin 5 phosphate and flavin adenine dinucleotide. Riboflavin 5 phosphate has the highest bioavailability.
Vitamin B3
There are 3 forms of vitamin B3: Niacin, Niacinamide (also called Nicotinamide) and the new form Nicotinamide Riboside (NR). All of these are highly absorbable.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin. In supplements, pyridoxal HCL and pyridoxamine-5-phosphate (P5P) are used. P5P is the active form of vitamin B6. Several side effects are known from pyridoxal. This is not the case with P5P. Therefore, choose a supplement that contains pyridoxamine-5-phosphate.
Vitamin B9/11 (folate)
Folic acid is the most common form of folate used in dietary supplements. However, a significant percentage of the population has difficulty converting folic acid into folate. It is better to choose a supplement with the active form, in such cases it is methylfolate.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 comes in the forms methylcobalamin, adenosylcobalamin, hydroxycobalamin and cyanocobalamin. Only methyl and adenosylcobalamin are the active forms.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin. Many different forms of vitamin C are available in supplements, including ascorbic acid (the cheapest and most commonly used form of vitamin C) and the (non-acidic) form of mineral ascorbate. Mineral ascorbate is vitamin C bound to a mineral such as calcium or magnesium. Mineral ascorbates have better bioavailability than ascorbic acid.

Vitamin D
Vitamin D exists in two forms: ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3). Vitamin D3 is the biologically active form and is the more potent of the two: it increases blood levels of vitamin D twice as much as D2 does. Vitamin D3 is also the form our body makes itself when the skin is exposed to sunlight.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin. Vitamin E is the collective name for a number of substances naturally present in food: the tocopherols, such as alpha, beta, gamma or delta-tocopherol. The cells absorb alpha-tocopherol best and is therefore by far the most effective form of vitamin E.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin. Vitamin K occurs as two subtypes (vitamins), both of which are required for the full function of vitamin K.[1] Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) is a plant form commonly found in vegetables. Vitamin K2 (menaquinone) is a form made by bacteria in fermentation.
Vitamin K2 comes in different forms. In supplements, you'll often find MK-4 or MK-7.
An effective vitamin K formula therefore contains both forms of vitamin K.
Which nutrients work best together?
Some nutrients stimulate the absorption of others. These are some well-known combinations:
- Vitamin D and calcium
- Vitamin B12 and folate
- Zinc and copper
- Iron and vitamin C
- Vitamins A, D, E or K and fats
Note: Zinc and Copper do not stimulate each other's absorption; they are in competition with each other. Both minerals must therefore be present in the right proportion to each other for both to be properly absorbable.
Good supplement formulas contain useful combinations of vitamins so that you get maximum benefit from the action of the substances present.
Vitamins A, D, E and K are fat-soluble vitamins. They are better absorbed when combined with fat. You can boost absorption by taking these vitamins with fat-rich food, or (even easier) by taking a supplement where the vitamin is dissolved in fat.

What are chelated minerals?
Minerals are unstable and are better absorbed when coupled with an amino acid or an organic acid. This is called a chelated mineral. Examples of chelated minerals are magnesium taurate (magnesium bound to taurate), copper citrate (copper bound to citric acid) and chromium picolinate (chromium bound to picolinic acid).
Still, chelated minerals are no guarantee of success. Chelated minerals often contain more of the other compound than of the mineral itself. For example, magnesium citrate may be only 13% magnesium and magnesium taurate 10%. Therefore, it is important that the label is transparent in how much of the mineral you take in.
A good label states "Magnesium (as magnesium taurate) 25 mg", so you know you are taking in 25 mg. A misleading label shows "Magnesium taurate 250 mg", making you think you are taking in much more magnesium than the 25 mg it contains (since the remaining 175 mg is taurate and not magnesium).
Which supplement forms does the body use best?
Animal organs (such as liver, kidneys, heart) are enormously rich in nutrients. They contain exactly the forms that our organs also use and therefore have high bioavailability.
Our organs need many vitamins and minerals to perform their functions. In the past, we used to eat organ meat and thus got a lot of valuable nutrients. Nowadays, most people don't like organ meat and avoid it in their diet.
Fortunately, there are more and more freeze-dried organ meat supplements on the market. The advantage is that you get both high-quality multivitamins and also avoid the taste of organ meat.
What are excipients in supplements?
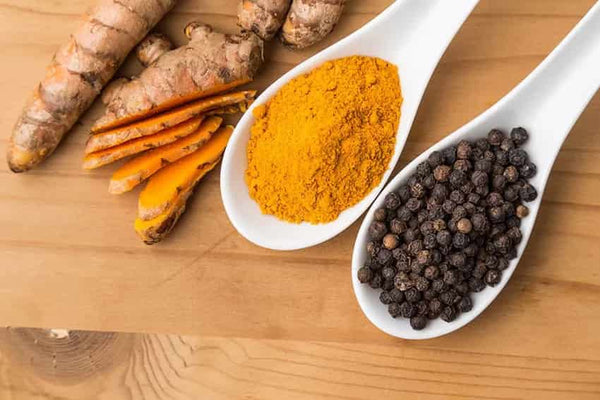

Herbs and other herbal substances are usually quickly broken down by the liver. They are often combined with other substances that increase absorption. One well-known substance is piperine, which is made from black pepper.
Piperine, like grapefruit, reduces the action of certain liver enzymes. When you combine piperine with curcumin, you increase bioavailability by up to 2000%. However, you should be careful with piperine and grapefruit if you are taking certain medicines. Consult your doctor when considering a supplement with black pepper or grapefruit.
Another example is the combination of Fisetin and fibre from Fenugreek. This slows down digestion and increases bioavailability 25 times. This technique is also used with curcumin.
What is the best way to extract mushrooms?
The benefits of herbs and mushrooms come from specific substances. The bioavailability of these substances is often not good if you were to eat the herbs or mushrooms unprocessed. Or you would have to eat a lot of them to experience a beneficial effect. That is why extraction is used. This involves dissolving the active substance in water, alcohol or oil.
Dual extraction is the best method. That is extraction with water and then with alcohol. It allows you to extract both the water-soluble and non-water-soluble substances from the mushroom.
You can go one step further by using sound waves (Ultrasonic Assisted Extraction). Ultrasonic sound waves break open the cell walls, making the substances even more available.
What are liposomal supplements?
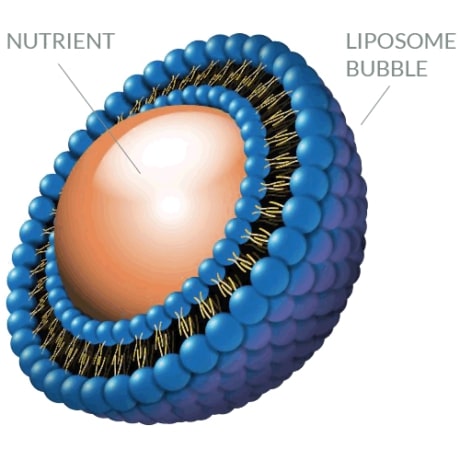
A new trend in the supplement industry is the use of liposomes. Liposomes are envelopes made of a thin layer of fat or phospholipids. You can fill them with all kinds of substances, such as vitamins and herbal extracts. The advantage is that liposomes enter the bloodstream without digestion so the contents are immediately available to your body.
Another advantage of liposomal supplements is their liquid form. This is convenient if you prefer not to swallow capsules or tablets.
Conclusion
Bioavailability is an important selection criteria when choosing a supplement: it is an indicator of the quality of a supplement. Many factors influence the bioavailability of supplements. Therefore, read the label carefully!
Supplements with high bioavailability are usually more expensive. However, it is wiser to buy more expensive supplements that will benefit your body than to take cheaper ones that are useless.
Besides bioavailability, there are other aspects that influence the quality and therefore the price of supplements. For instance, that they are free of allergens, toxins, GMO, gluten and fillers.
Want supplements of the highest quality? Then go to LiveHelfi. We select the best products in the market for your convenience.











